Create rabbitMQ Cluster
In this lab we will deploy a RabbitMQ workload that is created with the Catalog.
Enabling RabbitMQ
As an Admin go to the Apps panel and activate RabbitMQ, afterwards click the deploy button.
If you are not and Admin then ask your Admin to enable the RabbitMQ application.
Creating a RabbitMQ Cluster
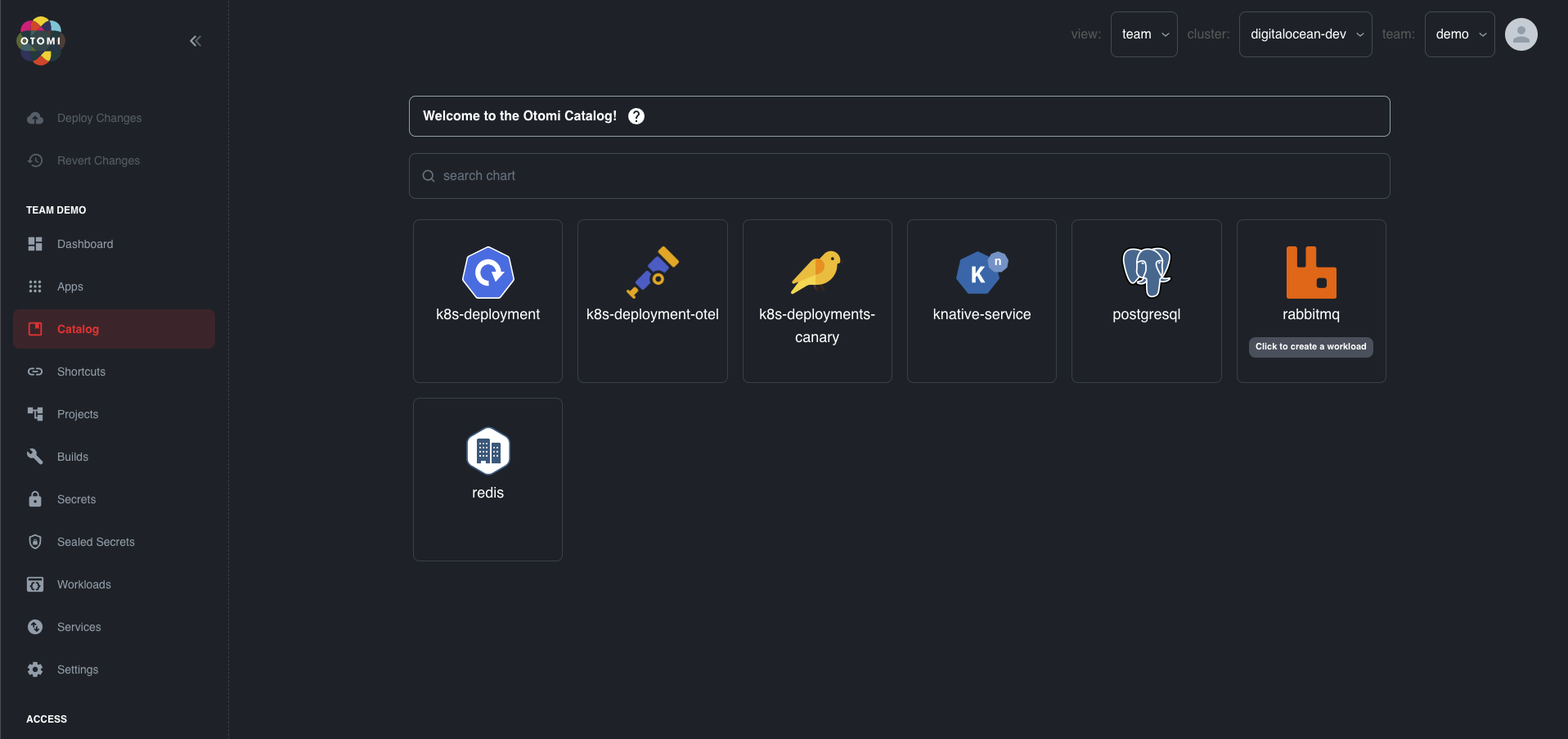
To create a RabbitMQ Cluster, on the team overview click on the Catalog in the sidebar and select the RabbitMQ workload. This will take you to the page with the readme where you can see all specifications and definitions that you can use to create your RabbitMQ Cluster with Queues and Policies.
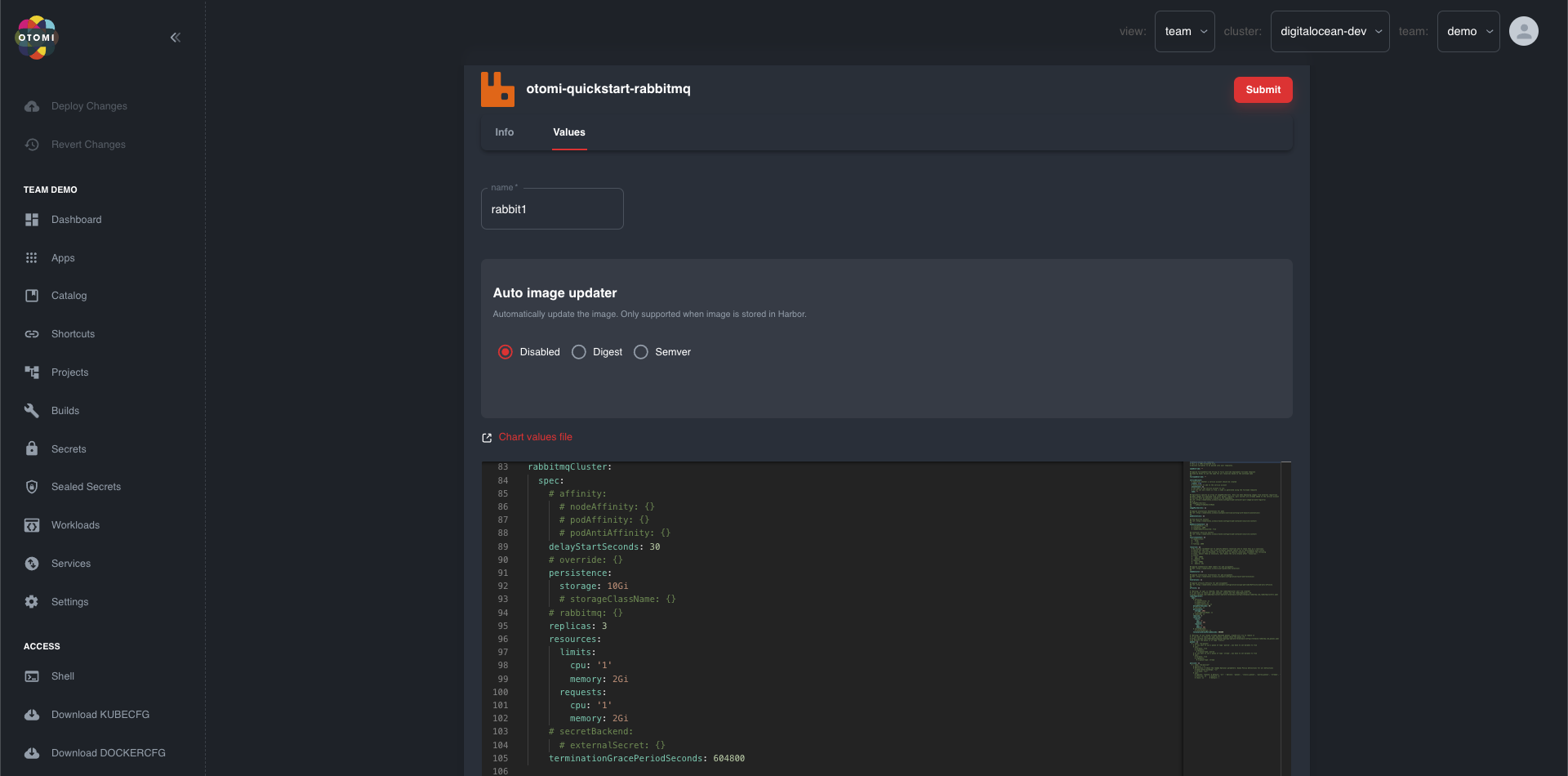
To configure the RabbitMQ Cluster workload go to the Values tab and fill in a name for the RabbitMQ Cluster workload. Afterwards you can scroll down an edit the cluster parameters.
Adding Queues and Policies
To configure Queues and Policies for the rabbitMQ Cluster you can add them to the queues and policies parameters respectively.
For example, we create a rabbitMQ Cluster workload with the name rabbit1 with 2 queues and 2 policies.
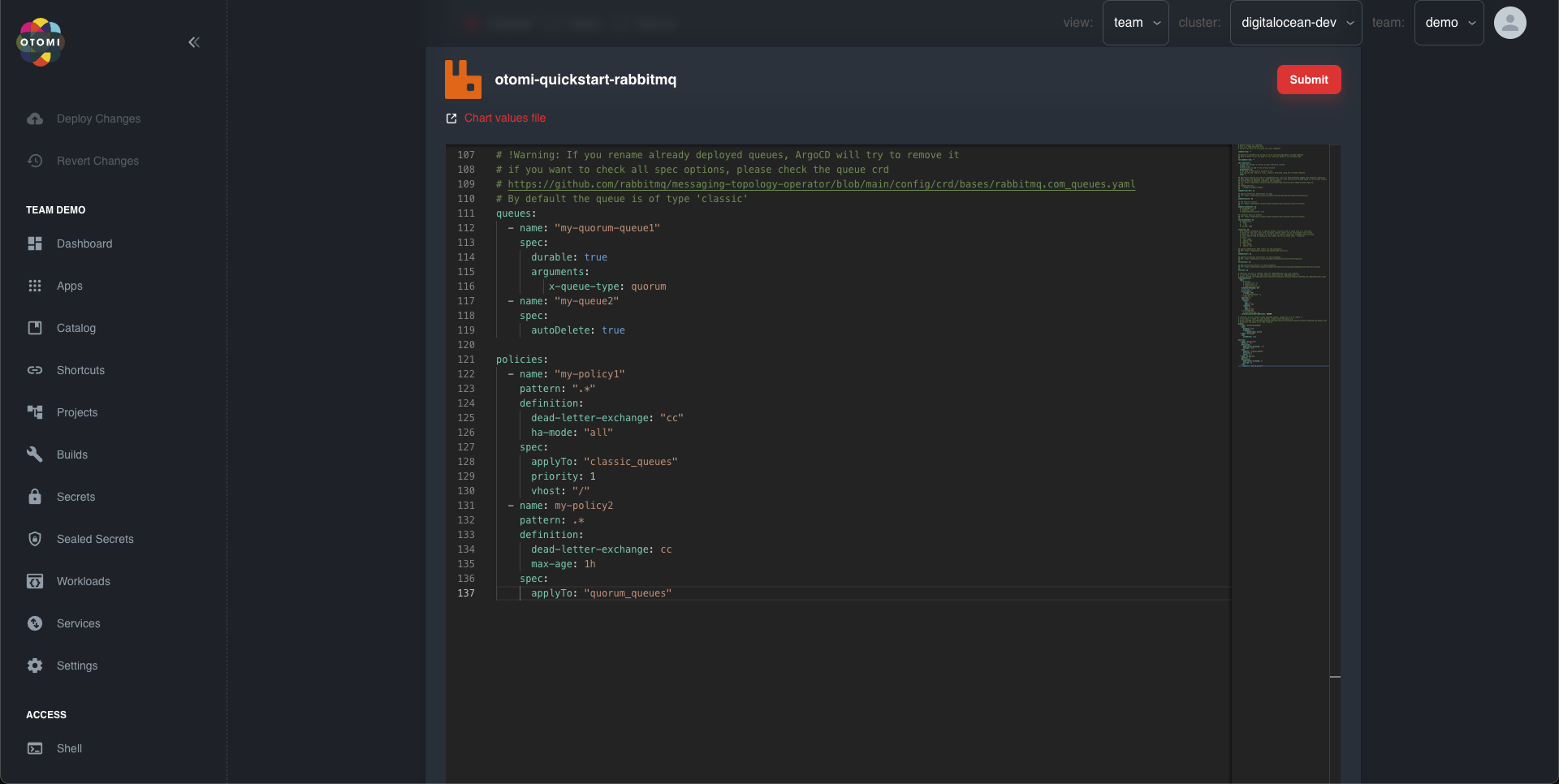
Do remember that even though these values can be edited afterwards, not all specifications or definitions can be updated after a queue or policy has been created. Please make sure everything is filled in correctly.
queues:
- name: my-quorum-queue1
spec:
durable: true
arguments:
x-queue-type: quorum
- name: my-quorum-queue2
spec:
arguments:
autoDelete: true
policies:
- name: my-policy1
pattern: ".*"
definition:
dead-letter-exchange: cc
ha-mode: all
spec:
applyTo: classic_queues
priority: 1
vhost: "/"
- name: my-policy2
pattern: ".*"
definition:
dead-letter-exchange: cc
max-age: 1h
spec:
applyTo: quorum_queues
When everything is filled in correctly you can submit and click the deploy changes button.
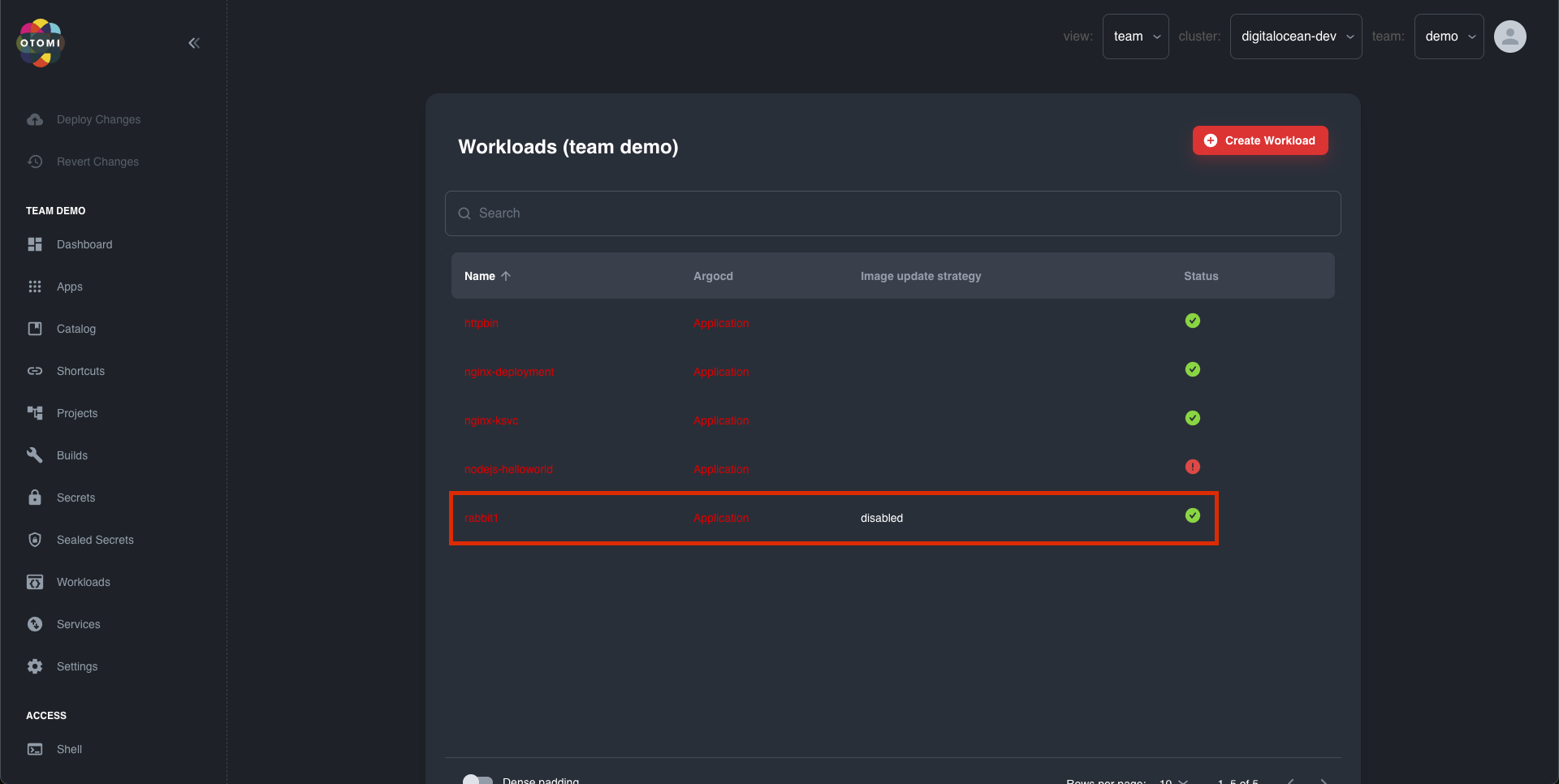
To check the status of the deployment you can go to the workload list page.
Workload Status:
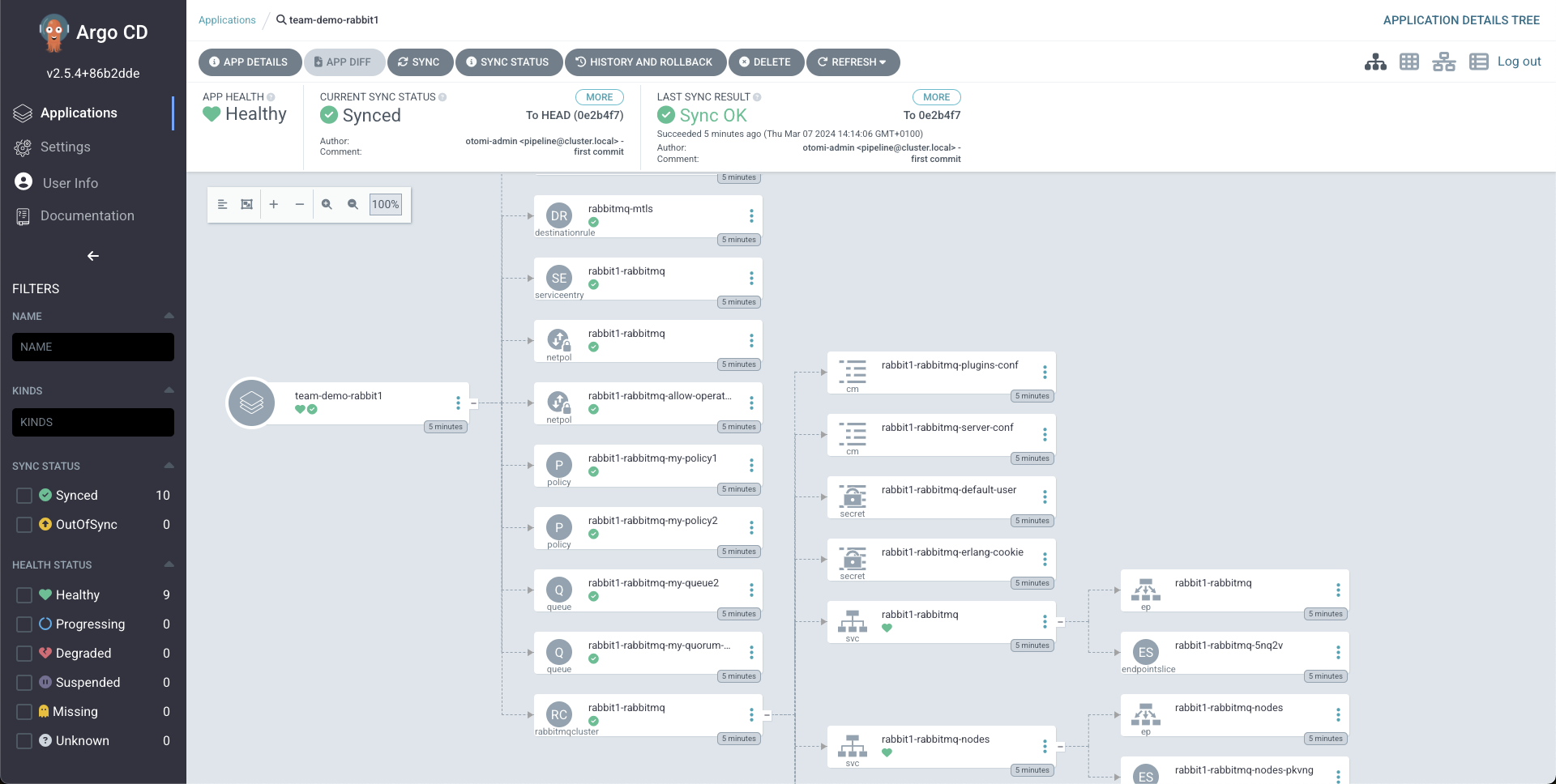
ArgoCD Status:
Accessing the RabbitMQ Management UI
To access the RabbitMQ Management UI you have two options:
- retrieve the default user credentials and
port-forwardtherabbitMQ server. - Create a service to expose the
rabbitMQ serverand access theManagement UIpublicly. This is not recommended for production services
In this lab we are going to use the cluster. To do this connect to your k8s cluster with kubectl.
In this example the rabbitMQ cluster was created in the demo team so we have to get the secret from the team-demo namespace. Please retrieve the secret from the namespace where the rabbitMQ cluster was created.
To retrieve the username and decode it from base64 use the following command:
kubectl get secret rabbit1-rabbitmq-default-user -n team-demo -o jsonpath="{.data.username}" | base64 --decode
To retrieve the password and decode it from base64 use the following command:
kubectl get secret rabbit1-rabbitmq-default-user -n team-demo -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 --decode
Which looks like the this:

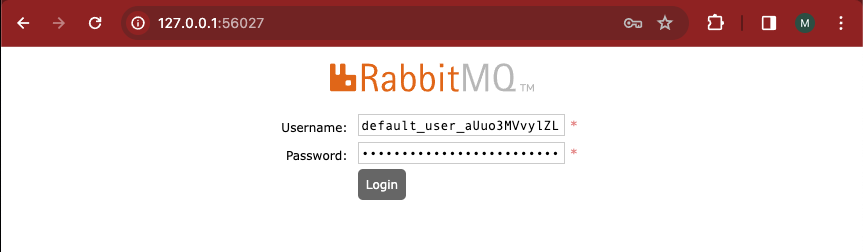
Make sure you don't copy the % symbol at the end.
Now you have to port-forward the rabbitmq container with port number 15672 that is inside the rabbitmq pod called rabbit1-rabbitmq-server-0 to a port of your choice that is not used, I use port 56027 for this example.
rabbit1-rabbitmq-server-0 has the prefix rabbit1 because this is the name that we gave it when creating the workload.
To port-forward use the following command:
kubectl port-forward -n team-demo rabbit1-rabbitmq-server-0 56027:15672
Access http://localhost:56027 and use the previously acquired user credentials to log in. If you cannot log in, please check if the credentials are for the correct rabbitMQ cluster.
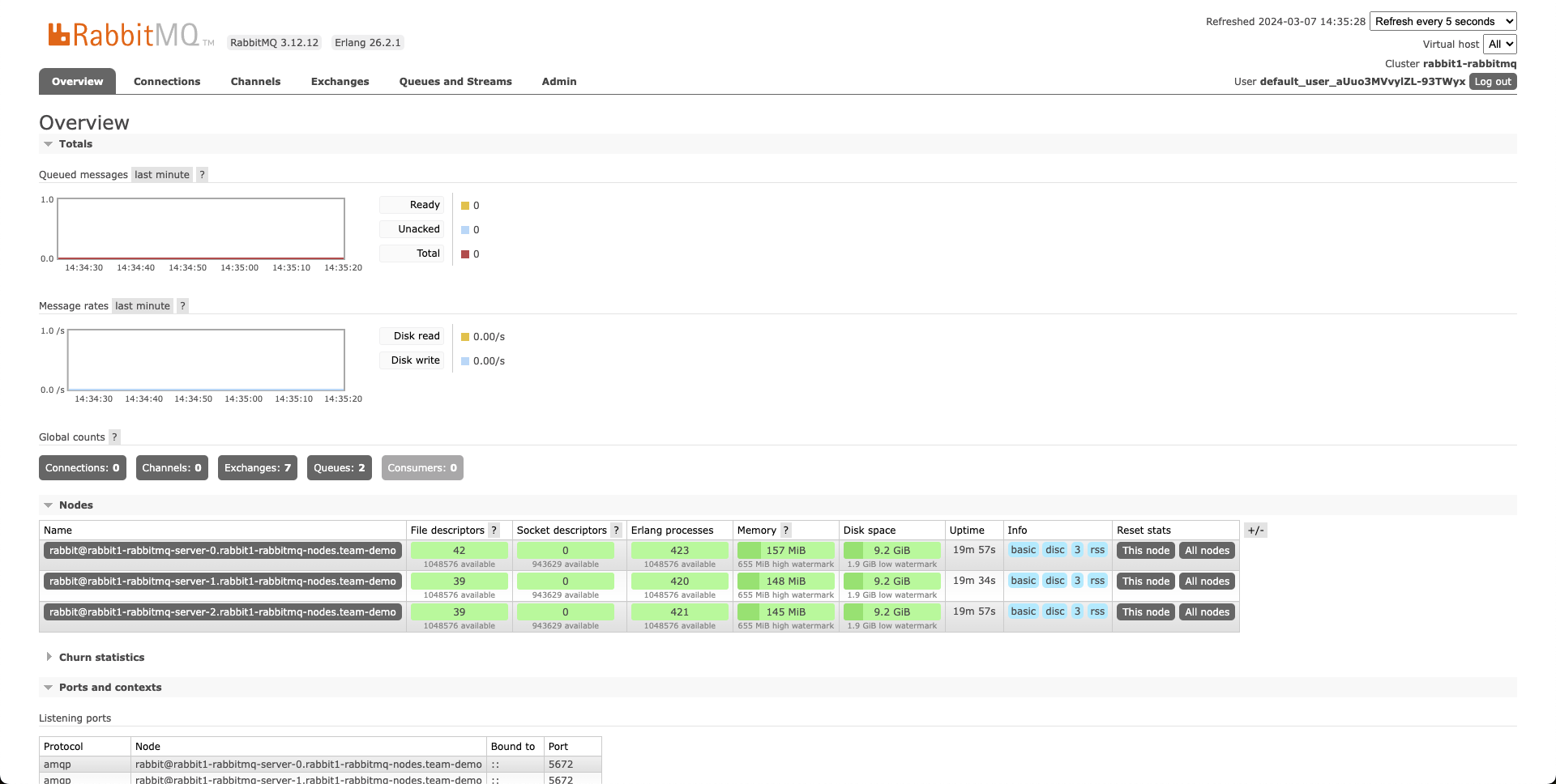
Checking the RabbitMQ Management UI
Now that we are logged in you should see the following:
We can also check the queues that we specified when creating the rabbitmq cluster in the Queues and Streams tab.
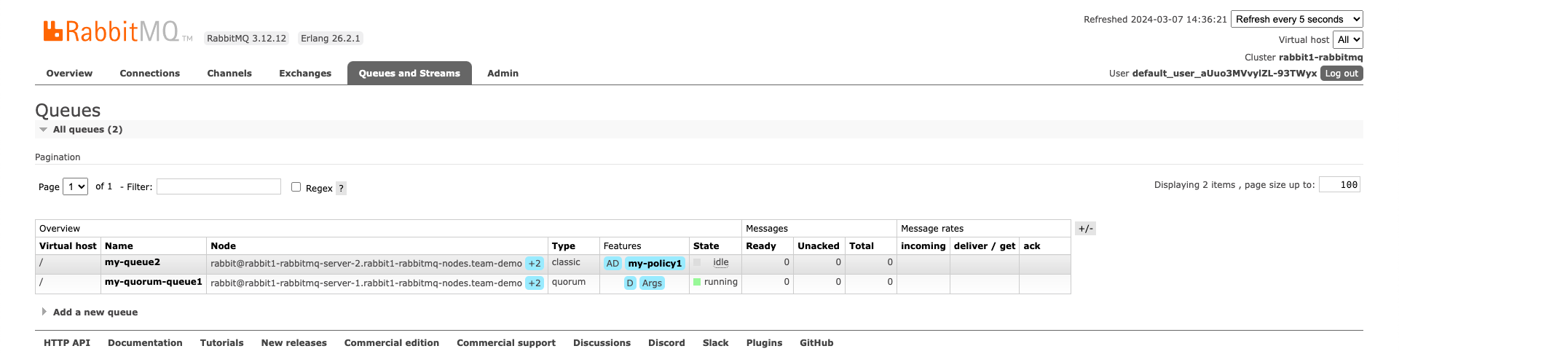
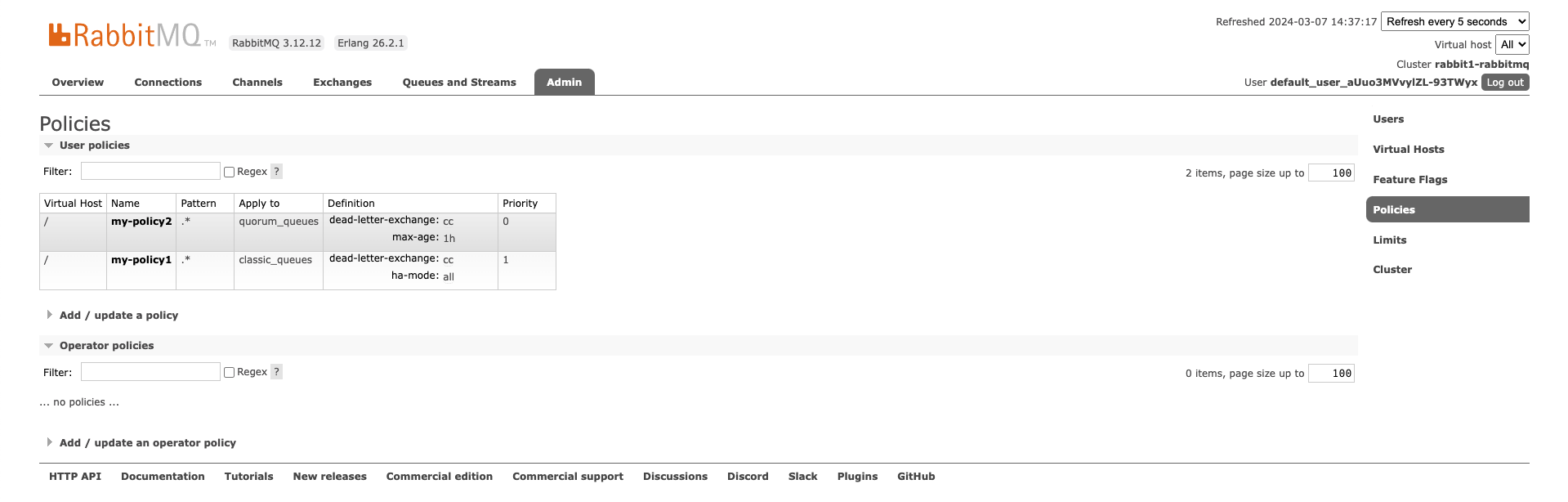
To see the policies that we defined you can see them in the Admin tab and under Policies:
Connecting an Application to the rabbitMQ Cluster
Will be expanded upon
To connect to the rabbitMQ cluster you use AMQP to open a connection. To open a connection you need to create a connection string using the username, password, host and port of the rabbitmq cluster.
To get the host use the following command:
kubectl get secret rabbit1-rabbitmq-default-user -n team-demo -o jsonpath="{.data.host}" | base64 --decode
To get the port use the following command:
kubectl get secret rabbit1-rabbitmq-default-user -n team-demo -o jsonpath="{.data.port}" | base64 --decode
The connection string is build like this:
amqp://USERNAME:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/
With values:
amqp://default_user_mWPUECo5wsbtpgY3oze:MdzUL4CcgF-cQryLfk5uxqf57qqWBG8l@matthew-rabbit1-rabbitmq.team-admin.svc:5672/